Waiting for customers to pay their outstanding invoices? You’re not alone. Invoice factoring can help.
Most invoices are set to payment terms of 30 to 90 days, meaning that from the day an invoice is sent to your customer, you’re unlikely to see that money for at least a month, if not longer. These long payment cycles put many small business owners in a constant cash crunch, making it hard to keep up with critical expenses like payroll, utilities, or inventory. That likely prevents you from investing in growth opportunities or maintaining day-to-day operations that keep everything on track.
This guide will answer all of your questions about invoice factoring, helping you determine if it’s a good fit for your business.
Key Takeaways
- Invoice Factoring Provides Immediate Cash Flow: Invoice factoring is the process of selling your unpaid invoices at a discount in exchange for a cash advance, helping you better manage cash flow without waiting for customer payments.
- Factoring Costs Vary: Invoice factoring rates typically range from 1% – 5% and are based on how much you plan to factor, your customers’ creditworthiness, and the average age of your receivables.
- Factoring Helps Businesses Grow: Factoring is a good fit for businesses that cannot qualify for a loan or line of credit, struggle with slow-paying customers, or need quick access to working capital.
What Is Invoice Factoring?
Invoice factoring is a form of alternative financing that involves selling your outstanding invoices to a third party (factoring company) in exchange for cash up front.
Because it’s a sale, not a loan, it doesn’t impact your credit like traditional bank financing. It also allows small businesses to unlock the cash value of their invoices long before their customers pay their bills. To prevent any confusion, the term “factoring” is often used interchangeably with “accounts receivable financing”.
What Is a Factoring Company?
A factoring company (or “factor”) is a financing partner that purchases your invoices in exchange for cash.
Once you are approved to work with the factor, you can sell your outstanding receivables in order to boost working capital and avoid the delay of long payment terms. The factoring company verifies your invoices, funds up to 90% of the invoice face value, then collects on those invoices directly from your customers (via a notice of assignment). Once the factor collects from the end customer on the standard payment terms, they release the remainder of the invoice value to you, minus a small factoring fee – typically one to five percent.
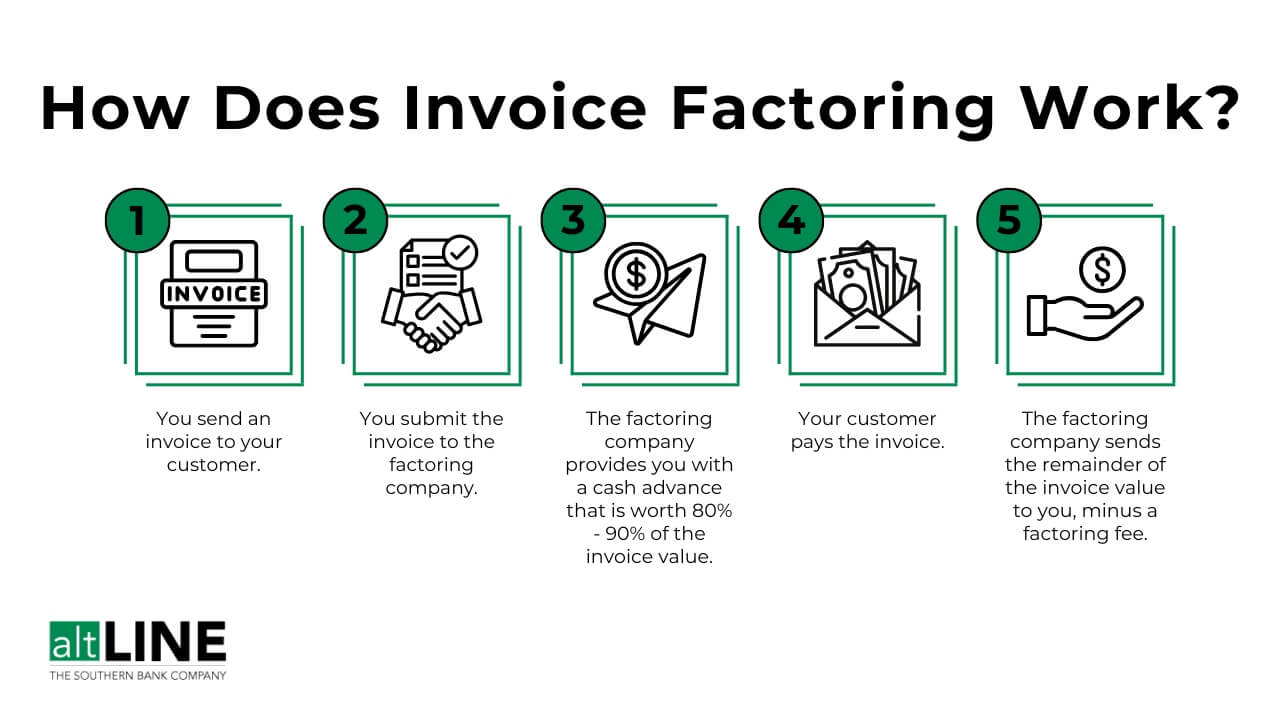
How Does Invoice Factoring Work?
Factoring is a fairly simple and straight forward type of financing. Once you understand the process, you can determine if it makes sense for your business.
Here’s how invoice factoring works:
- The Seller, after delivering a service or product, submits an outstanding customer invoice to a factoring company for funding.
- The factoring company immediately advances the majority of the invoice value (anywhere from 80-100%, depending on the industry) to the seller. This typically occurs within 24 hours.
- Any remaining funds are released to the seller once the debtor submits payment to the factoring company.
 Invoice Factoring Example
Invoice Factoring Example
Here’s a more in-depth look at how the invoice factoring process works.
Scenario
XYZ Manufacturing is a business that produces custom parts for companies in the automotive industry. XYZ recently completed a $100,000 order for a client and sent an invoice that is due in 30 days. However, XYZ Manufacturing is growing quickly and needs cash to pay for the raw materials and wages for the next round of production. Waiting 30 days for invoice payment will delay the business’s operations, which could result in lost business opportunities.
Solution
To fill the cash flow gap, XYZ Manufacturing decides to work with an invoice factoring company. The company offers the following terms:
- 90% advance rate
- 2% factoring rate
XYZ factors its outstanding $100,000 invoice. The factoring company sends XYZ Manufacturing $90,000 immediately (90% of $100,000) that the manufacturer can use to begin work on the next round of production.
From there, the factoring company takes over the invoice. After 30 days, XYZ’s client pays the full $100,000 directly to the factoring company. Upon payment collection, the factoring company sends the remaining invoice value to XYZ Manufacturing, minus the 2% factoring fee. This results in XYZ Manufacturing receiving $8,000 once the invoice is paid ($100,000 minus the $90,000 advance and the $2,000 factoring fee).
Below is a breakdown of the numbers:
| Description | Amount |
|---|---|
| Factored Invoice Value | $100,000 |
| Advance Rate | 90% |
| Factoring Rate | 2% |
| Initial Cash Advance Sent to XYZ Manufacturing | $90,000 |
| Fee Collected by the Factoring Company | $2,000 |
| Remaining Cash Sent to XYZ Manufacturing Once the Invoice Is Paid | $8,000 |
| Total Money XYZ Manufacturing Receives | $98,000 |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Factoring?
While there are many positives to invoice factoring, there are also downsides, depending on the nature of your small business and the factoring partner you choose to work with. Here, we’ll break down the pros and cons of factoring so you can see the full picture.
Advantages of Factoring
- Quick invoice factoring grants immediate access to cash for your business
- Easier and faster approval than traditional bank lending
- Many of your once-time consuming accounting responsibilities are handled by the factoring company
Disadvantages of Factoring
- Slightly reduced profit margins on factored invoices
- Hidden costs and fees if you work with a bad factoring company
- Unless working on a non-notification factoring agreement, debtors have to be notified of third-party involvement
Need Cash Quickly?
How to Qualify for Factoring
In order to qualify for factoring, your company will need to have the following items:
- Invoices to factor
- Creditworthy clients
- A completed factoring application – apply now
- An accounts receivable aging report
- A business bank account
- A tax ID number
- A form of personal identification
Are Factored Receivables Subject to Taxes?
So, invoice factoring presents many potential advantages for a company. But how does quick factoring fit into the tax system in the United States? This relationship is somewhat complex. For business owners, it can be difficult to identify whether factored receivables are subject to taxes payable to the federal government.
The IRS considers several factors in determining whether any factored receivables qualify as taxable. The purpose of this determination is to prevent firms from using invoice factoring to transfer income overseas or engage in tax avoidance or tax evasion regarding the use of invoicing.
Common Invoice Factoring Myths and Misconceptions
You may have heard some bad things about invoice factoring, potentially from someone who has used it before and had a bad experience. While there are certainly better factoring companies than others, and some that will try to take advantage of you, here are a few things about invoice factoring that aren’t true.
- It’s only good for struggling businesses: Not true! Factoring can be a great cash flow solution for businesses of all sizes and stages of growth. For example, many large companies employ factoring simply to reduce debt.
- It’s too expensive to be sustainable: While factoring is typically more expensive than traditional loans, most businesses that are a good fit for factoring have pricing power, meaning that they can incrementally increase their prices to compensate for factoring costs.
- You can’t use factoring if you have bad credit: Wrong! Invoice factoring is often the best fit for businesses with bad credit. That’s because factoring companies really only care about the creditworthiness of your customers (because they’re the ones paying the invoices), not you as a business.
- All factors are the same: Every factoring company is different. Some will try to take advantage of you with hidden fees, float, and other added costs that make factoring unsustainably expensive and unpredictable. Factors like altLINE don’t do that – as a regulated bank, we’re 100% transparent because we have to be, and we want to be.
Independent Factoring Companies vs. Bank Factoring Companies
While the overall goal of invoice factoring is the same, choosing the right provider is critical. Know that there are two types of providers: those that are independent and those that are backed by a bank.
Independent Factoring Company
An independent factoring company can provide immediate funds for your outstanding invoices, but they must borrow from a third party in order to fund your invoices. That can increase risk and costs for your business and can reduce efficiency. Plus, they aren’t FDIC-insured and as heavily regulated as bank factors, which makes it easier for independent factors to act in predatory manners.
Much of any perceived negative stigma surrounding factoring is due to independent, unregulated actors taking advantage of borrowers.
Bank Factoring Company
A bank factor provides the same flexibility and benefits as an independent factor, but they offer additional advantages.
- Easier transition to bank loan: A bank factor works with many businesses who have been told “no” by a bank for a commercial loan, but they are still strong candidates for working with a bank that offers factoring, or accounts receivable financing. Businesses that work with a bank owned factoring company may also have an easier time transitioning to a commercial loan at a later date.
- Greater security: Banks that are federally regulated and FDIC-insured are more secure and provide a sense of financial stability for businesses. A bank offers a level of comfort not found in independent alternative financing companies like BlueVine or Fundbox. Clients feel better about interacting with a bank than an unfamiliar or unknown business entity.
- Competitive rates: Since banks use their own funds, they can offer the business very competitive rates. Unlike many independent factoring companies who work with multiple funding sources, a bank acts as a direct source of funds and eliminates the middleman.
What Are the Different Types of Invoice Factoring?
Let’s look into each type of factoring so you know exactly what you’re looking for when you’re finding a factoring company to work with.
Recourse Factoring
If your customer fails to pay their invoice to the factor, you must pay back the recourse factoring company for the amount advanced. While this adds risk for you, recourse factors offer lower fees. For reference, altLINE is a recourse factor.
Non-Recourse Factoring
In non-recourse factoring, if your customer fails to pay their invoice to the factor, the factor assumes responsibility for the loss, not your business. This is lower risk for you but generally comes with higher factoring fees.
Spot Factoring
Spot factoring allows you to factor only one invoice. Let’s say you have one large outstanding invoice that you need paid now, a spot factor will fund that one invoice alone.
Whole Ledger Factoring
Whole ledger factoring means that the factoring company requires that you are factoring all of your invoices together. Some businesses don’t have payment delay issues across all customers, so this may not be preferable.
Disclosed Factoring
Disclosed factoring is where borrowers’ customers (the debtors) are aware of the factoring agreement in place. The customers receive a Notice of Assignment, informing them they are to pay the factoring company moving forward, rather than their vendor (the borrower).
Non-Notification Factoring
Non-notification factoring, also known as confidential invoice factoring or undisclosed factoring, occurs when borrowers’ customers (the debtors) are not aware of a factoring agreement in place. With non-notification factoring, the factor would refrain from sending a Notice of Assignment to the debtor. Instead, they communicate with debtors as though it is an extension of the borrowing business.
What Industries Benefit Most From Factoring Invoices?
Generally, factoring works best for small B2B businesses and startups within the following industries:
- Staffing
- Transportation and Trucking
- Manufacturing
- Janitorial Services
- Wholesale and Distribution
- Consulting
- Oil and Gas
- Professional Services
- Food and Beverage
- Apparel Companies
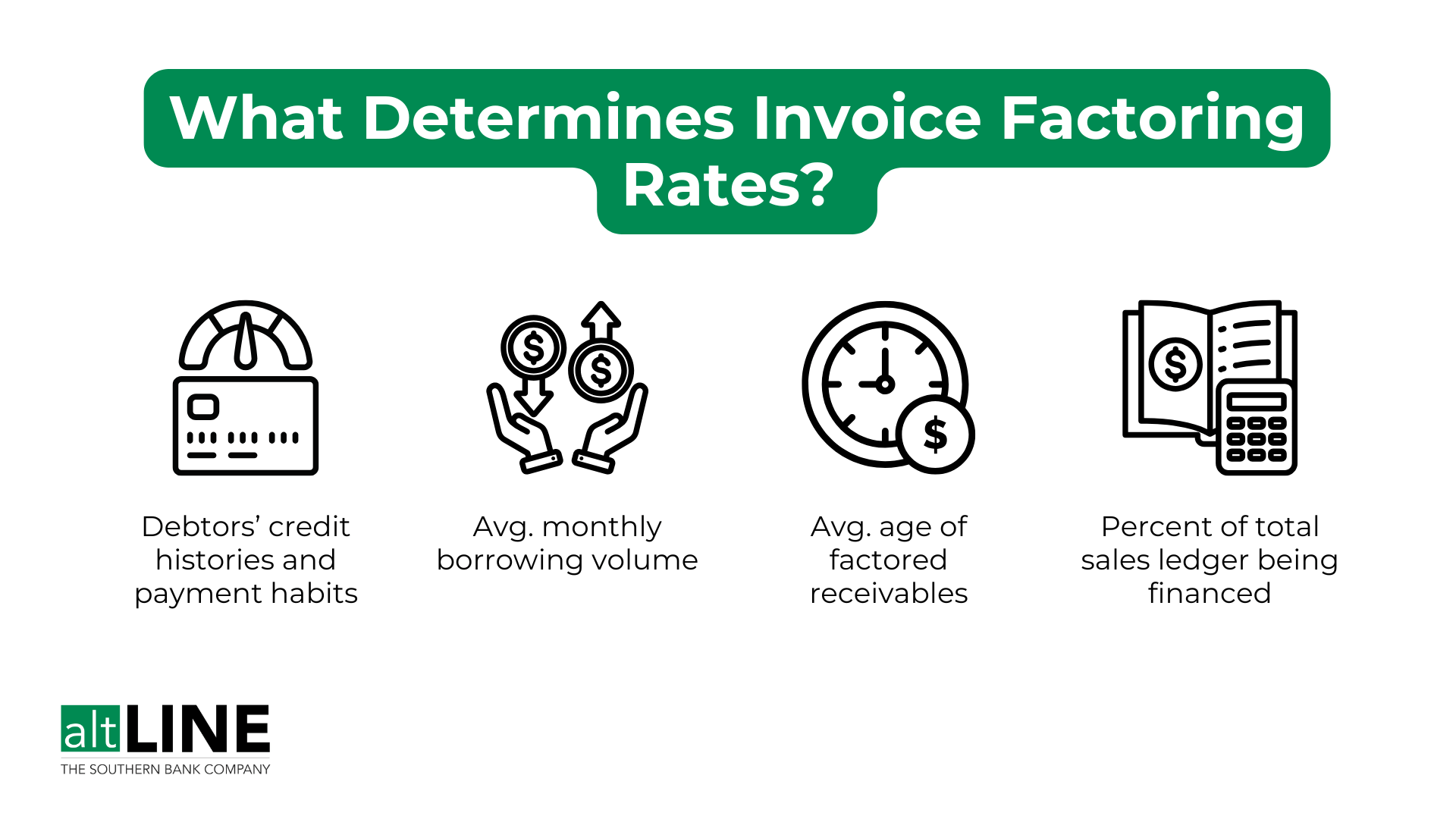
How Much Does Factoring Cost? Rates, Fees & Structures
Invoice factoring rates tend to range from 1% – 5%, but there are many aspects that go into determining the rate structure. The main drivers that influence factoring fees are:
- The creditworthiness of your customers (also called “debtors”)
- The size of your borrowing need
- Invoice amount and the age of your receivables
- Whether all or only select invoices will be financed
Additionally, factoring rates often follow a tiered structure, meaning the factoring company sets different rates depending on how long it takes the customer to pay. The fee typically increases in stages, based on the aging of the invoice.
Slightly reduced profit margins can be a reason some decide not to move forward with factoring.
However, according to altLINE VP of Operations Kelley Burnett, most business owners pondering factoring see the back-office accounting work that a factoring company like altLINE performs as making up for any lost dollars.
“We have a whole staff that’s calling their customers, verifying invoices, vetting their potential new customers—there is a lot of accounting labor on our end that benefits a company,” Burnett said. “Business owners can view us as an extension of their team. Instead of having to hire someone for accounts receivable, they’re basically outsourcing it to us.”
For more information on how tiered factoring structures work, read our full article on understanding invoice factoring rates.
Beware of Hidden Fees and Float in the Factoring Agreement
Many independent factoring companies will try to charge you hidden fees buried deep inside your factoring agreement. Make sure you read your contract thoroughly and ask questions about anything that looks suspicious – it will save you time and money in the long run.
The best invoice factoring companies will be 100% transparent with their customers, like altLINE. As a bank, we’re fully regulated and are both unable and unwilling to deceive our factoring customers. That said, watch out for these kinds of hidden fees from other companies:
- Monthly minimum fees
- Maintenance fees
- Cancellation or termination fees
- Float days and fees
- Due diligence fees
For more information about these specific fees and what they mean, read our full articles on understand invoice factoring agreements and invoice factoring float and other hidden fees explained.
How to Choose the Best Factoring Company
When you start browsing factoring companies (or if you’re looking to switch factoring companies), you’ll find there are tons of options. You’re obviously researching for the best factoring company, but how do you go about it?
Remember the difference between independent factors and bank factors. It’s best to prioritize finding a bank factor.
Factoring vs. Similar Types of Alternative Financing
While there are many types of small business loans and alternative financing out there, not all are a fit for every business.
Invoice Factoring vs. Invoice Financing
The main difference between invoice factoring and invoice financing, also known as AR financing, lies in the underwriting criteria of the deal structures. While factoring offers greater flexibility, AR financing has more strictness around the credit profile. Consequently, AR financing typically offers preferred financing terms.
Another key difference between invoice factoring vs. invoice financing is who eventually collects on your invoices. With invoice financing, you retain control of collection. In invoice factoring, however, the factoring company assumes the role of collecting on the invoices they purchased. Other than the collection process (i.e. assignment), both forms of financing are nearly identical. Many providers will offer both factoring and AR financing.
Invoice Factoring vs. Invoice Discounting
A common misconception is that invoice factoring and invoice discounting are the same thing. While they are similar, there are some key differences. Mainly, factoring is a transparent process and invoice discounting is more confidential. Read our full article on invoice discounting for more information.
Is Invoice Factoring a Fit for Your Business to Improve Cash Flow?
Cash flow is the lifeblood of a business, and it can determine if the business grows or dies. If you’re considering invoice factoring, it probably means you’re looking for quick and reliable source of funding. Factoring can do just that: quickly turning your receivables into cash.
But what makes your business a good fit for invoice factoring? If you meet any or all of the characteristics below, it may be the right solution for your business.
- Do you have B2B customers?
- Do you offer payment terms between 30 and 90 days?
- Do you have fair or poor credit?
- Does your business have limited operating history?
- Do you have few or no assets to borrow against?
These are each legitimate reasons to consider invoice factoring.
Ready to Get Your Free Quote?
Once you submit your quote request, a representative will be in touch with you within 24 hours. We move quickly so that your business keeps growing.









